Classical Faulting Theory
Classical faulting theory postulates that the maximum compressive stress is
oriented approxamately 30 degrees to the failure plane based on the following
equations and illustrations.
Byerlee's Law
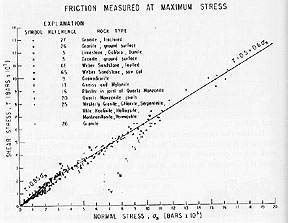
The coeffient of sliding friction for most rock types was experimetally
determined to be ~0.6-0.8. The best fit line in the diagram defines the
failure envelope used in Mohr Circle analysis.
 From Davis and Reynolds
From Davis and Reynolds
Mohr Circle equations and the Coulomb equation are used to
determine the ideal angle between maximum stress and the failue plane,
which is referred to as theta. When a friction coefficient of ~0.7 is used
theta equals 30 degrees.
next page.
 From Davis and Reynolds
From Davis and Reynolds
 From Davis and Reynolds
From Davis and Reynolds